LinkedHashSet Tutorials In Java With Example
LinkedHashSet is a type of Collection, which takes all the functionalities of HashSet class, that it does not allow duplicate elements to be stored and allow null elements in it.
As LinkedHashSet extends HashSet class so it also indirectly extends AbstractSet Class And implements Set Interface.
Everything in LinkedHashSet including the basic structure that we get from AbstractSet class, all the methods that are defined in HashSet is extended from its parent class.
Important Note: Hash set does not maintains the insertion order, that is when we retrieve values from it we do not get that values in the same order we have entered in it. So, The functionality of maintaining the insertion order is added into LinkedHashSet and to attain this functionality it uses doubly-linked list. This doubly-linked list maintains the iteration ordering, which is in general the order in which values are added in the set. Apart from adding this functionality of maintaining insertion order, it do not add any new method of its own.
Table of Contents
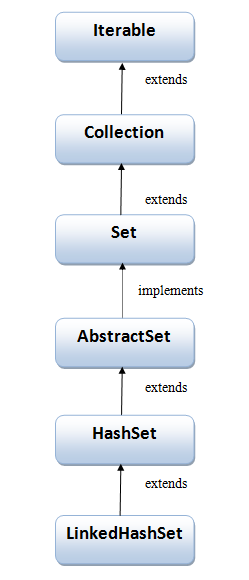
Hierarchy of LinkedHashSet Class
LinkedHashSet Class extends HashSet Class which further extends AbstractSet Class and implements Set Interface. Set Interface further extends Collection Interface and Iterable Interface, as shown in figure below:
Example of LinkedHashSet Class
Let us discuss LinkedHashset class with the help of program, following program has been divided into 3 Steps that we will discuss one by one:
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedHashSetDemo
{
public static void main(String args[]){
//Step 1:
LinkedHashSet<String> linkedHashSetObject1= new LinkedHashSet<String>();
LinkedHashSet<Integer> linkedHashSetObject2= new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();
//Step 2:
linkedHashSetObject1.add("I");
linkedHashSetObject1.add("Love");
linkedHashSetObject1.add("Java");
linkedHashSetObject1.add("Java");
linkedHashSetObject1.add("I");
linkedHashSetObject2.add(9);
linkedHashSetObject2.add(3);
linkedHashSetObject2.add(4);
linkedHashSetObject2.add(9);
linkedHashSetObject2.add(5);
linkedHashSetObject2.add(9);
//step 3:
System.out.println("Values in Linked HashSet String object are:" +linkedHashSetObject1);
System.out.println("Values in Linked HashSet Inteeger object are:"
+linkedHashSetObject2);
}
}
Output:
Values in Linked HashSet String object are:[I, Love, Java] Values in Linked HashSet Inteeger object are:[9, 3, 4, 5]
Description:
From output, it is clear that linked hash set maintains insertion order, and do not allow duplicate values.
- In Step 1, we have created two objects of LinkedHashSet collection, we have defined these objects to store value of String type and Integer type.
- In Step 2, we have used add method to store values in the data structures that we have created in step 1.
- In Step 3, we have printed values of these objects, and found that linkedHashSet does not store duplicate values, and maintains insertion order.
Important Points About LinkedHashSet
- LinkedHashSet is similar to HashSet that only stores unique values, that is duplicate values are not allowed.
- LinkedHashSet maintains insertion order, which means it returns the elements in the order in which they are added.
- It does not do any kind of sorting to the stored values.
- LinkedHashSet is similar to HashSet which allows only one null value in it, As duplicates are not allowed.
- LinkedHashSet uses hash table to store the values.
Quick Revision Points About LinkedHashSet
- It Maintains Insertion Order using Doubly Linked List.
- No duplicate values are allowed.
- Only one null value can be stored.
- Uses HashTable to store values.
- No new Method is added in this class, all are extended from HashSet.
Recent Posts
- Boolean Class in JAVA with Example
- Difference Between String And StringBuffer in JAVA With Example
- String Tokenizer in JAVA with example
- Life Cycle of a Thread In JAVA
- Creating a Thread in Java with Example
Premium Project Source Code:
- Food Ordering Android App Project Source Code
- Ecommerce Store Android App Project Source Code
- Convert Website Into Android App Project Source Code
- Quiz Game Android App Project Source Code
- Radio Streaming Android App Source Code
- City Guide Android App Project Source Code
- QR Barcode Android App Project Source Code