Inheritance Tutorial With Example In JAVA
Inheritance is a mechanism that allows the class to use the states and behavior of another class. In simple words a class derive field and methods from another class. The derived class in inheritance is called sub class (also called derived class or extended class, or child class) and the class from which it is derived is called super class (also called base class or a parent class).
Important Note: A super class can have any number of sub class in inheritance but sub class can only extend one super class. Multiple inheritance is not supported in JAVA.
Inheritance is one of the important concept of object oriented programming. The simple definition says inheritance provides mechanism that allows a class to inherit properties of another class.
Inheritance Concept: Inheritance means inherit the properties and behavior of existing object in a new object.
Way To Achieve Inheritance: It is achieved by deriving a new class from existing class using extends keyword. Example, Class Child extends Base { }.
Table of Contents
Explanation With Example:
- In Inheritance by default all data members and member functions of a parent class are available to child class if they are not private
- Inheritance defines is-a relationship between a super class(parent) and its sub class(child).
- extends keyword is used to show inheritance in java.
For example :
Suppose a class name Base.java
class Base
{
//Code of Base class
}
Another class Child.java use Inheritance to extends properties from Base class.
Class Child extends Base
{
//extends the properties of base class
}
In the above example, Child class will inherit field and methods of Base class.
Types Of Inheritance
There are 3 types of inheritance:
- Single Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
1. Single Inheritance:
In Single inheritance one class is derived from one parent class. The below diagram shows single inheritance where Class B inherits from Class A.
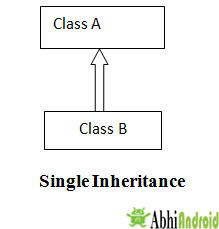
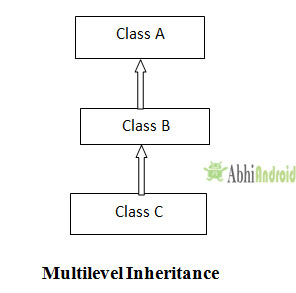
In multilevel inheritance there is a concept of grand parent class as shown in below diagram class C inherits class B and class B inherits class A.
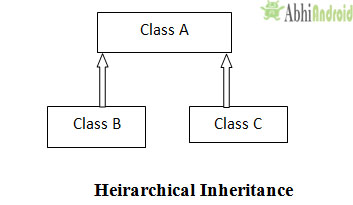
In Hierarchical inheritance more than one sub classes is derived from a single parent class as shown in below diagram class B and C both are derived from single parent class A.
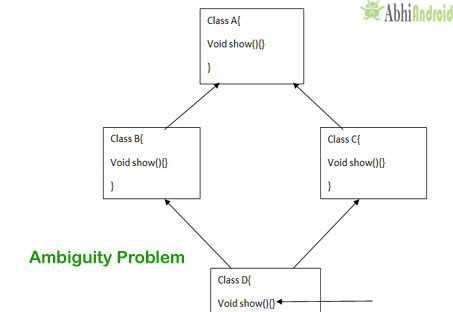
Why multiple inheritance is not supported in java:
To remove ambiguity:
Multiple inheritance is not supported in java as it causes ambiguity in few scenarios. The most common scenario is Diamond problem.
Inheritance Example:
Below is the program to show you the use of inheritance in java. For coding this we have used eclipse IDE.
Example 1: Let’s inherit some fields and methods in Child class from Base class.
Base class is having 2 fields and 1 method:
class Base
{
int x=50;
int y = 60;
//Addition method return integer value of x+y
public int addition(){
return x+y; //return 110
}
}
Child class inherit addition method and x field from Base class:
public class Child extends Base
{
int z;
public void subtraction(){
//addition method and x filed is inherited from Base Class
z = addition() - x;
System.out.println(z);
}
}
In the Main class we create Child object and calls subtraction method on it.
public class InheritanceAbhiandroid {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child child = new Child(); //Child object
child.subtraction();//Subtraction method called on child object
}
}
Output:
60
Example 2:
Base.java:
class Base
{
int x=50;
}
Child.java:
public class Child extends Base
{
int x=20;
void show()
{
System.out.println(x);
}
}
InheritanceAbhiandroid.java
public class InheritanceAbhiandroid {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
c.show();
}
}
OUTPUT:
20
Important Note: The above program prints value of x=20 because priority always goes to local variables. So in show() method of child class,we can access member of parent class i.e base class using super keyword. It means if we want to print value of x=50 also from the same above program then by using super keyword.
Example 3 of Inheritance using super keyword:
Base.java:
class Base
{
int x=50;
}
Child.java:
class Child extends Base
{
int x=20;
void show()
{
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(super.x);
}
}
public class InheritanceAbhiAndroid{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Child c=new Child();
c.show();
}
}
OUTPUT:
20 50
Importance Of Inheritance:
- Reusuability of code: It is one of the important feature of inheritance. It is a good way to reuse the already existing code rather than creating the same code again and again. This feature not only saves time and money as we are reusing the properties but it also increase reliability of code.
- Method Overriding: With the help of inheritance, it is possible to override the methods of base class so that base class method is easily used in derived class.
Inheritance Important Points To Remember:
- Whenever a parent class and a child class both are having same data members then this concept is known as data hiding.
- Whenever a parent class and a child class both are having ditto same functions then this concept is known as method overriding.
- Whenever a parent class and a child class both are having same static functions then this concept is known as function hiding.
- We cannot print super, there is a syntax error. Always data members of parent class is inherited by super
- If you make any non static function of a class as final then it cannot be overridden by the child class that means to stop method overriding makes a function final.
Inheritance Quick Revision:
- Inheritance allows the class to use the states and behavior of another class using extends keyword
- Inheritance is-a relationship between a Base class and its child class.
- Multiple inheritance is not supported in JAVA.
Recent Posts
- Boolean Class in JAVA with Example
- Difference Between String And StringBuffer in JAVA With Example
- String Tokenizer in JAVA with example
- Life Cycle of a Thread In JAVA
- Creating a Thread in Java with Example
Premium Project Source Code:
- Food Ordering Android App Project Source Code
- Ecommerce Store Android App Project Source Code
- Convert Website Into Android App Project Source Code
- Quiz Game Android App Project Source Code
- Radio Streaming Android App Source Code
- City Guide Android App Project Source Code
- QR Barcode Android App Project Source Code
Leave a Reply