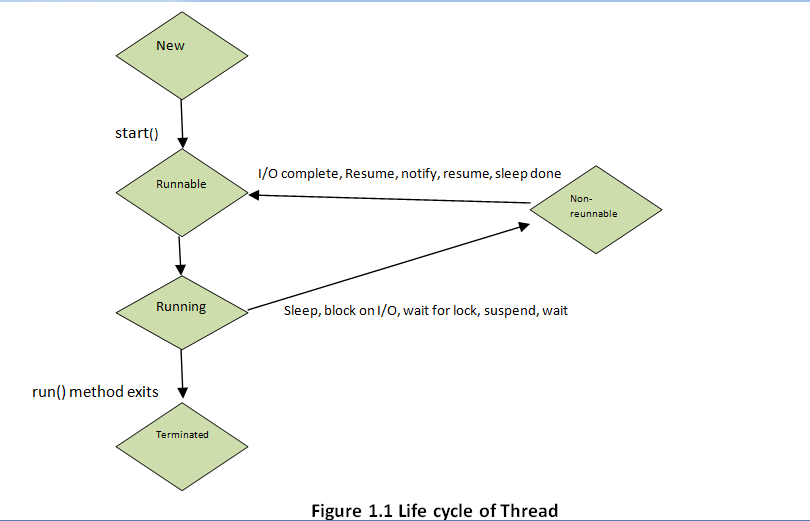
In Multithreading, Thread can be in one of the five states which forms life cycle of the Thread. This life cycle of a thread is controlled by java virtual machine (JVM).
Following are the five stages by which Thread goes through in its lifecycle as shown in figure 1.1 :
- New
- Runnable
- Running
- Non-Runnable (Blocked)
- Terminated
Let us discuss each Stage in Detail One by one:
1. New
In this stage thread is referred to as a born thread. A new thread starts its life cycle in this stage. The thread remains in this thread until programs starts the thread.
2. Runnable
After a newly born thread is started , the thread comes in this stage which is referred to as runnable. The thread comes into this stage after calling start() method, Thread scheduler sets it to be runnable.
3. Running
Thread is in running stage only when Thread Scheduler has selected it. It executes all the tasks assigned to it in this stage.
4. Non-Runnable (Blocked)
In this stage, Thread is still alive but it is not eligible to run due to some condition. In this stage thread is referred to be in waiting stage.
5. Terminated
Thread is terminated when its run() method exists. In this stage thread is referred as Dead thread.