JSON Parsing Tutorial With Example In Android Studio [Step by Step]
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation. It is structured, light weight, human readable and easy to parse. It’s a best alternative to XML when our android app needs to interchange data from server. XML parsing is very complex as compare to JSON parsing.
JSON is shorter, quicker and easier way to interchange data from server. JSON is great success and most of the API available support JSON format.
Android Provide us four different classes to manipulate JSON data. These classes are JSONObject, JSONArray, JSONStringer and JSONTokenizer.
Table Of Contents
Sample JSON format:
Below is the sample code of JSON. Its very simple JSON code which gives us the list of users where each object contain the information like user id, name, email, gender and different contact numbers.
{
"users": [
{
"id": "1087",
"name": "Abhishek Saini",
"email": "info@abhiandroid.com",
"gender" : "male",
"contact": {
"mobile": "+91 0000000000",
"home": "00 000000",
"office": "00 000000"
}
},
{
"id": "1088",
"name": "Gourav",
"email": "gourav9188@gmail.com",
"gender" : "male",
"contact": {
"mobile": "+91 0000000000",
"home": "00 000000",
"office": "00 000000"
}
},
.
.
.
.
]
}
JSON Elements In Android:
In Android, JSON consist of many components. Below we define some common components.
1. Array([): In a JSON, square bracket ([) represents a JSONArray. JSONArray values may be any mix of JSONObjects, other JSONArrays, Strings, Booleans, Integers, Longs, Doubles, null or NULL. Values may not be NaNs, infinities, or of any type not listed here.
2. Objects({): In a JSON, curly bracket ({) represents a JSONObject. A JSONObject represents the data in the form of key and value pair. JSONObject values may be any mix of other JSONObjects, JSONArrays, Strings, Booleans, Integers, Longs, Doubles, null or NULL. Values may not be NaNs, infinities, or of any type not listed here.
3. key: A JSONObject contains a key that is in string format. A pair of key and value creates a JSONObject.
4. Value: Each key has a value that could be primitive datatype(integer, float, String etc).
JSON Parsing In Android:
Usually, JSON contain two types of nodes JSONArray and JSONObject so while parsing we have to use the appropriate method. If JSON starts from square bracket ([) we use getJSONArray() method and if it start from curly bracket ({) then we should use the getJSONObject() method. Apart from these there are some other methods for better parsing JSON data.
JSONObjet Parsing methods:
Below we define some important methods of JSONObject parsing which are mainly used for parsing the data from JSONObject.
1. get(String name): This method is used to get the value from JSONObject. It returns the value of object type. We pass the String type key and it returns the value of Object type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
2. getBoolean(String name): This method is used to get the Boolean value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns the value of Boolean type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
3. getDouble(String name): This method is used to get the double type value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns the value in double type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
4. getInt(String name): This method is used to get the int type value from JSONObject. We pass the string type key and it returns the value in int type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
5. getJSONArray(String name): This method is used to get the JSONArray type value. We pass the String type key and it returns JSONArray if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
6. getJSONObject(String name): This method is used to get the JSONObject type value. We pass the String type key and it returns the JSONObject value if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
7. getLong(String name): This method is used to get the long type value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns the value in long type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
8. getString(String name): This method is used to get the String type value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns the value in String type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
9. length(): This method is used to get the number of name/value mappings in this object.
10. keys(): This method is used to get the iterator of String names in the Object.
11. opt(String name): This method is used to get the value from JSONObject. It returns the value of Object type. We pass the String type key and it returns the value of Object type if exists otherwise it returns null.
12. optBoolean(String name): This method is used to get the Boolean value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns the value of Boolean type if exists otherwise it returns false.
13. optDouble(String name): This method is used to get the double type value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns the value in double type if exists otherwise it returns NaN.
14. optInt(String name): This method is used to get the int type value from JSONObject. We pass the string type key and it returns the value in int type if exists otherwise it returns 0.
15. optJSONArray(String name): This method is used to get the JSONArray type value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns JSONArray if exists otherwise it returns null.
16. optJSONObject(String name): This method is used to get the other JSONObject type value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns the JSONObject value if exists otherwise it returns null.
17. optLong(String name): This method is used to get the long type value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns the value in long type if exists otherwise it returns 0.
18. optString(String name): This method is used to get the String type value from JSONObject. We pass the String type key and it returns the value in String type if exists otherwise it returns emptly(“”) string.
JSONArray Parsing methods:
Below we define some important methods of JSONArray parsing which are mainly used for parsing the data from JSONArray.
1. get(int index): This method is used to get the value from JSONArray. It returns the value of object type. We pass the index and it returns the value of object type if exist otherwise it throws JSONException.
2. getBoolean(int index): This method is used to get the Boolean value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value of Boolean type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
3. getDouble(int index): This method is used to get the double type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value in double type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
4. getInt(int index): This method is used to get the int type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value in int type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
5. getJSONArray(int index): This method is used to get the JSONArray type value. We pass the index and it returns JSONArray if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
6. getJSONObject(int index): This method is used to get the JSONObject type value. We pass the index and it returns the JSONObject value if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
7. getLong(int index): This method is used to get the long type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value in long type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
8. getString(int index): This method is used to get the String type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value in String type if exists otherwise it throws JSONException.
9. length(): This method is used to get the number of values in this Array.
10. opt(int index): This method is used to get the value from JSONArray. It returns the value of Object type. We pass the index and it returns the value at index of Object type if exists otherwise it returns null.
11. optBoolean(int index): This method is used to get the Boolean value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value of Boolean type if exists otherwise it returns false.
12. optDouble(int index): This method is used to get the double type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value in double type if exists otherwise it returns NaN.
13. optInt(int index): This method is used to get the int type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value in int type if exists otherwise it returns 0.
14. optJSONArray(int index): This method is used to get the other JSONArray type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns JSONArray if exists otherwise it returns null.
15. optJSONObject(int index): This method is used to get the JSONObject type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the JSONObject value if exists otherwise it returns null.
16. optLong(int index): This method is used to get the long type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value in long type if exists otherwise it returns 0.
17. optString(int index): This method is used to get the String type value from JSONArray. We pass the index and it returns the value in String type if exists otherwise it returns empty(“”) string.
Example 1 of Simple JSON Parsing In Android Studio:
Below is the example of JSON parsing in Android, In this example we parse the data from JSON and then display it in the UI.In this, we have employee name and salary stored in JSON format. Firstly we create two TextView‘s in our XML file and then in our Activity we parse the data using JSONObject methods and set it in the TextView‘s.
Below you can download code, see final output and step by step explanation of the example:

Step 1: Create a new project and name it JSONParsingExample.
Step 2: Open res -> layout -> activity_main.xml (or) main.xml and add following code:
In this step we create two TextView‘s for displaying employee name and salary.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="abhiandroid.com.jsonparsingexample.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:text="Name"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/salary"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="80dp"
android:text="Salary"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</RelativeLayout>
Step 3 : Now open app -> java -> package -> MainActivity.java and add the below code.
In this step firstly we get the reference of both TextView’s then we parse the JSON using JSONObject methods and finally we set the data in Textview’s.
package abhiandroid.com.jsonparsingexample;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.widget.TextView;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
String JSON_STRING = "{\"employee\":{\"name\":\"Abhishek Saini\",\"salary\":65000}}";
String name, salary;
TextView employeeName, employeeSalary;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// get the reference of TextView's
employeeName = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.name);
employeeSalary = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.salary);
try {
// get JSONObject from JSON file
JSONObject obj = new JSONObject(JSON_STRING);
// fetch JSONObject named employee
JSONObject employee = obj.getJSONObject("employee");
// get employee name and salary
name = employee.getString("name");
salary = employee.getString("salary");
// set employee name and salary in TextView's
employeeName.setText("Name: "+name);
employeeSalary.setText("Salary: "+salary);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JSON Parsing File Example 2 In Android Studio:
Below is the 2nd example of JSON parsing In Android Studio. In this example we create a JSON file and store it in assets folder of Android. In this JSON file we have list of users where each object contain the information like user id, name, email, gender and different contact numbers. In this we are using LinearLayoutManager with vertical orientation to display the array items. Firstly we declare a RecyclerView in our XML file and then get the reference of it in our Activity. After that we fetch the JSON file then parse the JSONArray data and finally set the Adapter to show the items in RecyclerView. Whenever a user clicks on an item the name of the Person is displayed on the screen with the help of Toast.
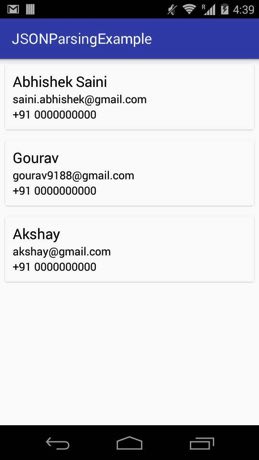
Step 1: Create a new project and name it JSONParsingExample.
Step 2: Open Gradle Scripts > build.gradle and add RecyclerView and CardView Library dependency in it.
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 24
buildToolsVersion "24.0.1"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "abhiandroid.com.jsonparsingexample"
minSdkVersion 16
targetSdkVersion 24
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:24.1.1'
compile "com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:23.0.1" // dependency file for RecyclerView
compile 'com.android.support:cardview-v7:23.0.1' // dependency file for CardView
}
Step 3: Open res -> layout -> activity_main.xml (or) main.xml and add following code:
In this step we create a RecyclerView in our XML file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="abhiandroid.com.jsonparsingexample.MainActivity">
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</RelativeLayout>
Step 4: Create a new XML file rowlayout.xml for item of RecyclerView and paste the following code in it.
In this step we create a new xml file for item row in which we create a TextView to show the data.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.v7.widget.CardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:card_view="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/card_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="10dp">
<!--
items for a single row of RecyclerView
-->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Name"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="20sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/email"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="email@email.com"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="15sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/mobileNo"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="e9999999999"
android:textColor="#000"
android:textSize="15sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</android.support.v7.widget.CardView>
Step 5 : Now open app -> java -> package -> MainActivity.java and add the below code.
In this step firstly we get the reference of RecyclerView. After that we fetch the JSON file from assets and parse the JSON data using JSONArray and JSONObject methods and then set a LayoutManager and finally we set the Adapter to show the items in RecyclerView.
package abhiandroid.com.jsonparsingexample;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.support.v7.widget.LinearLayoutManager;
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.util.Log;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
// ArrayList for person names, email Id's and mobile numbers
ArrayList<String> personNames = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> emailIds = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> mobileNumbers = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// get the reference of RecyclerView
RecyclerView recyclerView = (RecyclerView) findViewById(R.id.recyclerView);
// set a LinearLayoutManager with default vertical orientation
LinearLayoutManager linearLayoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(getApplicationContext());
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(linearLayoutManager);
try {
// get JSONObject from JSON file
JSONObject obj = new JSONObject(loadJSONFromAsset());
// fetch JSONArray named users
JSONArray userArray = obj.getJSONArray("users");
// implement for loop for getting users list data
for (int i = 0; i < userArray.length(); i++) {
// create a JSONObject for fetching single user data
JSONObject userDetail = userArray.getJSONObject(i);
// fetch email and name and store it in arraylist
personNames.add(userDetail.getString("name"));
emailIds.add(userDetail.getString("email"));
// create a object for getting contact data from JSONObject
JSONObject contact = userDetail.getJSONObject("contact");
// fetch mobile number and store it in arraylist
mobileNumbers.add(contact.getString("mobile"));
}
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// call the constructor of CustomAdapter to send the reference and data to Adapter
CustomAdapter customAdapter = new CustomAdapter(MainActivity.this, personNames, emailIds, mobileNumbers);
recyclerView.setAdapter(customAdapter); // set the Adapter to RecyclerView
}
public String loadJSONFromAsset() {
String json = null;
try {
InputStream is = getAssets().open("users_list.json");
int size = is.available();
byte[] buffer = new byte[size];
is.read(buffer);
is.close();
json = new String(buffer, "UTF-8");
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
return json;
}
}
Step 6: Create a new class CustomAdapter.java inside package and add the following code.
In this step we create a CustomAdapter class and extends RecyclerView.Adapter class with ViewHolder in it. After that we implement the overrided methods and create a constructor for getting the data from Activity, In this custom Adapter two methods are more important first is onCreateViewHolder in which we inflate the layout item xml and pass it to View Holder and other is onBindViewHolder in which we set the data in the view’s with the help of ViewHolder.
package abhiandroid.com.jsonparsingexample;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CustomAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<CustomAdapter.MyViewHolder> {
ArrayList<String> personNames;
ArrayList<String> emailIds;
ArrayList<String> mobileNumbers;
Context context;
public CustomAdapter(Context context, ArrayList<String> personNames, ArrayList<String> emailIds, ArrayList<String> mobileNumbers) {
this.context = context;
this.personNames = personNames;
this.emailIds = emailIds;
this.mobileNumbers = mobileNumbers;
}
@Override
public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
// infalte the item Layout
View v = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()).inflate(R.layout.rowlayout, parent, false);
MyViewHolder vh = new MyViewHolder(v); // pass the view to View Holder
return vh;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(MyViewHolder holder, final int position) {
// set the data in items
holder.name.setText(personNames.get(position));
holder.email.setText(emailIds.get(position));
holder.mobileNo.setText(mobileNumbers.get(position));
// implement setOnClickListener event on item view.
holder.itemView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
// display a toast with person name on item click
Toast.makeText(context, personNames.get(position), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return personNames.size();
}
public class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
TextView name, email, mobileNo;// init the item view's
public MyViewHolder(View itemView) {
super(itemView);
// get the reference of item view's
name = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.name);
email = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.email);
mobileNo = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.mobileNo);
}
}
}
20 thoughts on “JSON Parsing Tutorial With Example In Android Studio [Step by Step]”
Leave a Reply
Premium Project Source Code:
- Food Ordering Android App Project Source Code
- Ecommerce Store Android App Project Source Code
- Convert Website Into Android App Project Source Code
- Quiz Game Android App Project Source Code
- Radio Streaming Android App Source Code
- City Guide Android App Project Source Code
- QR Barcode Android App Project Source Code
thank you so much probably one of the best tutorial about JSON
Please send me the code
Thanks, It is very useful data for me to understand the JSON Parsing…
Very nicely explained
Thank you so much, I’ve been trying to understand how to handle JSON for hours.
How to convert JSON to model .
Please help me about this topic.
how I write that json file which in assets folder and how to save into it because json file option is not in android studio please help me with that
How to create users_list.json file. you didn’t explain about it.
Step by step Syllbus send me sir
how we convert ArrayList into gson string and vise versa…
how we save data in recyclerview throgh the json array
thanks for you. this is a book i need.
nice work bro. can you plz make a tutorial on insert and fetch data to and from database(phpmyadmin) using json.
Where can i find the users_list.json oe please send it to my email
2-11 18:01:21.526 1147-5616/? E/AudioFlinger: read failed: framesRead=-1
12-11 18:01:21.532 1147-5616/? E/AudioFlinger: read failed: framesRead=-1
12-11 18:01:21.538 1147-5616/? E/AudioFlinger: read failed: framesRead=-1
Error
Hi
some time i open some project that framlayout and when open add frame layout i cant understand please help me about these type error.
Thanks in Advance
How to pass url in recycler view example
If possible , plz you can add the code of JSON using Volley and Http
Thanks,
Thank you , for your usefull work
Thank you.plase send me json file code in my mail id